What is THCA & How’s It Different from THC?
High Points
- THCA is the raw, non-psychoactive form of THC found in raw cannabis flower. It only becomes THC when exposed to heat or light, a process called decarboxylation.
- THCA is common in flower, vapes, and concentrates where it gets converted to THC when heated. Products like edibles and tinctures already contain THC because the THCA has been decarboxylated during processing.
- THCA is similar to CBD in that it's non-intoxicating but does have bioactive effects. Some people consider raw cannabis to be a "superfood," consuming fresh, raw, and unheated cannabis through juicing or smoothies.
Have you ever wondered why smoking cannabis produces psychoactive effects but eating raw flower does not? The answer lies in the difference between THCA and THC. Read on to learn more about:
- What is THCA & Where Does It Come From?
- THCA and Decarboxylation
- What are the Potential Benefits of THCA?
- THC vs THCA: What's the Difference?
- THCA Products Available
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is THCA & Where Does It Come From?
THCA, or delta9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is a natural compound found in raw cannabis flower. It’s the non-psychoactive precursor to THC, the infamous cannabinoid responsible for the cannabis high.1 Abundant in cannabis plants, THCA slowly converts into THC over time after the plants have been harvested. While it doesn’t produce intoxication, THCA may offer a variety of bioactive effects, with consumers eating fresh, raw, and unheated cannabis through juicing or smoothies.1


THCA and Decarboxylation
The process of turning THCA into THC is called decarboxylation. Decarboxylation can be accomplished through slow processes like exposure to sunlight and up to ten days of storage in oil or alcohol at room temperature. However, when you light your bud, the THCA rapidly converts to THC.1
So we know that THCA turns into THC through the application of heat or light, but why does that make such a huge change? This is primarily due to the way the molecules interact with your body’s endocannabinoid system–specifically the CB1 and CB2 receptors. THCA has an extra carbolic ring, making it too big to fit into the body’s CB1 receptor.2 However, the act of decarboxylation removes the extra carbolic ring found in THCA, turning it into THC. Since it’s smaller, THC is able to bind to the CB1 and CB2 receptors to create a range of physiological effects.2


What are the Potential Benefits of THCA?
THCA is similar to another cannabis compound, CBD, in that it's non-intoxicating, but it does have bioactive effects. Some potential benefits of THCA have been reported, including:
-
Anti-Neausea: Similar to THC, THCA may have anti-emetic and anti-nausea properties.3
-
Anti-Inflammatory: THCA exhibits possible anti-inflammatory activity around inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.4
-
Brain Health: THCA may act as a neuroprotectant, specifically in neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease5 and Huntington’s disease.6
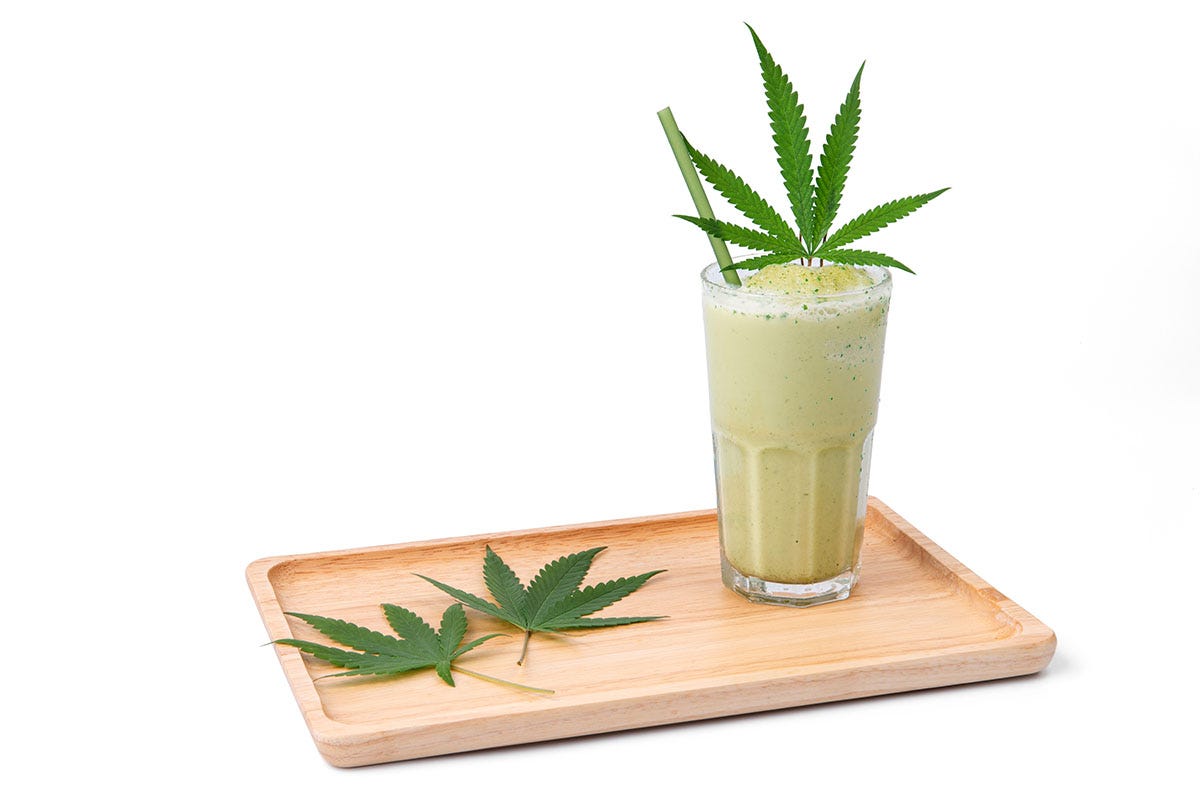


Some people consider raw cannabis to be a "superfood." Eating flower on its own probably won’t taste very good, which is why some THCA enthusiasts add it to juice or smoothies, similar to any other green vegetable.1
THC vs THCA: What’s the Difference?
The topic of THC vs THCA can cause quite a bit of confusion, especially when it comes to hemp-derived THCA. The explanation, though, is quite simple: raw cannabis flower contains THCA until you light it, and then it is converted into THC. Therefore, if you purchase a product that requires decarboxylation, the THCA will become THC.
THCA is a large molecule: too large to fit into cannabinoid receptors in the brain and central nervous system called CB1 receptors. When compared to THC, THCA has one more molecular carbolic ring, which makes it a misfit for CB1 receptors. In contrast, THC binds readily with these receptors, resulting in its psychoactive effects.1
THCA Products Available
The presence of THCA vs THC in products you purchase from a dispensary vary based on the type of product you buy.2
-
Edibles, Tinctures, Topicals: Your favorite dispensary gummies or tincture has already been decarboxylated during the manufacturing process, meaning the final product contains THC (and other labeled cannabinoids), and not THCA.
-
Vapes, Vape Cartridges, Disposable Vapes: The liquid inside the vape likely contains THCA, but that’s because it will be decarboxylated by the vape’s battery. The battery powers the heating element, which also turns the liquid into vapor.
-
Concentrates: While there are dozens of different concentrates available, they all have one thing in common: they need to be decarboxylated. Even THCA diamonds, which are just THC diamonds that haven’t been decarbed.2
-
Flower: THCA vs THC flower tends is the source of much confusion–specifically when it comes to legality. The raw flower you purchase at a dispensary contains THCA because it has not yet been decarboxylated. Once you light it, it becomes THC.


You may have seen THCA flower for sale outside of state-licensed dispensaries. How is this legal? Well, that’s the gray area thanks to the restrictions around marijuana-derived vs hemp-derived flower. THC products sold outside of dispensaries are typically derived from legal hemp. These products are made by converting CBD into THC through a chemical process,7 which is why they are sold in many places, even in states where cannabis is otherwise illegal.2


Frequently Asked Questions
THCA is a hot topic, so it’s natural to have questions. Here are a few common queries we get at our dispensaries.
Is THCA legal?
You can purchase THCA products from dispensaries in states that have legalized cannabis. While only THC is listed as a controlled substance, we don’t recommend purchasing THCA outside of a legal, reputable dispensary.
Does THCA get you “high”?
THCA doesn't get people "high." Its molecular makeup means that it can't bind to the CB1 receptors in our brain and central nervous system which produce intoxicating effects.
Is Delta 8 the same as THCA?
No, THCA is the acid precursor chemical to THC, and CBD is a different cannabinoid.
Is THCA the same as CBD?
No, THCA is the acid precursor chemical to THC, and CBD is a different cannabinoid.
What's the difference between THCA vs Delta-9?
Both THCA and THC are Delta 9 cannabinoids, but THCA is an acid, the precursor to THC.
What's the difference between THCA vs THCV?
THCV (Tetrahydrocannabivarin) is a different cannabinoid, discovered in 1971. It has similar chemical properties and effects to THC, not THCA.8


Understanding THCA
If you're interested in learning more about THCA and discovering the effects it may have for you, your budtender can discuss different strains of cannabis flower and concentrates like diamonds. They will be happy to assist you to select THCA products when you visit your local dispensary.
Sources
1. "THCA and THC: What's the difference?" June 20, 2022, https://weedmaps.com/learn/cannabis-and-your-body/difference-between-thca-thc
2. "What is THCA and what are the benefits of this cannabinoid?" Leafly, September 16, 2022, https://www.leafly.com/news/cannabis-101/what-is-thca-and-what-are-the-benefits-of-this-cannabinoid
3. “Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid reduces nausea-induced conditioned gaping in rats and vomiting in Suncus murinus,” PubMed Central, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3792001/
4. “Anti-Inflammatory Activity in Colon Models Is Derived from Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid That Interacts with Additional Compounds in Cannabis Extracts,” PubMed Central, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5627671/
5. “The Cannabinoids, CBDA and THCA, Rescue Memory Deficits and Reduce Amyloid-Beta and Tau Pathology in an Alzheimer’s Disease-like Mouse Model,” PubMed Central, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10095267/
6. “Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid is a potent PPARγ agonist with neuroprotective activity,” British Pharmacological Society, https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/bph.14019
7. “Extraction Explained: What Happens to In-Process Hemp Products?,” Cannabis Business Times, January 29, 2021, https://www.cannabisbusinesstimes.com/hemp/news/15690563/extraction-explained-what-happens-to-in-process-hemp-products
8. "THCA," Leafly, https://www.leafly.com/learn/cannabis-glossary/thcv